As a practicing M&A attorney representing both strategic acquirers and venture-backed targets, I have had a front row seat to the fundamental transformation of Silicon Valley’s exit landscape. The rise of acquihiring represents more than a market trend, it’s an evolutionary response to capital scarcity, talent wars, and regulatory uncertainty that demands sophisticated legal frameworks and innovation-friendly policy approaches.
As we come to the midpoint of Summer 2025, the tech industry continues to lay off staff, as big tech companies implement strategic workforce reductions. These layoffs are the result of the quick and efficient integration of artificial intelligence (AI), as firms restructure, phasing out roles in the process. Additional factors include cost-cutting initiatives, operational streamlining, and performance-based cuts targeting underperforming employees.
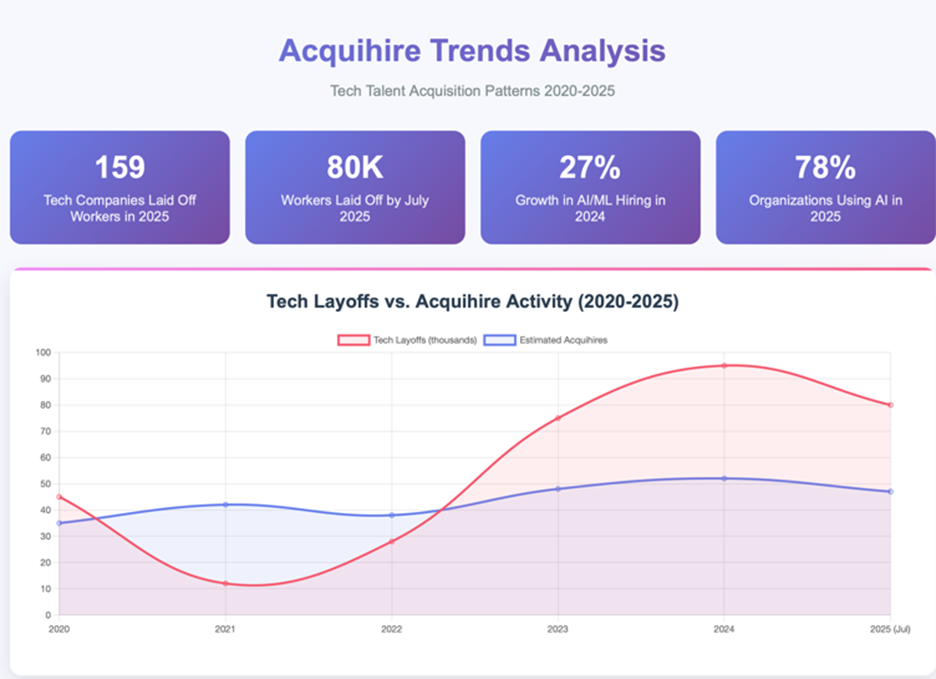
According to Layoffs. fyi, 159 tech companies laid off approximately 80,000 workers as of July 17, 2025. This follows a 2024 trend where at least 95,000 U.S.-based tech workers lost jobs, per Crunchbase data.
Amid frozen funding rounds and startup pivots, a familiar deal structure is gaining traction: the acquihire. For startups stuck between seed and Series A funding, an acquihire, where the company is acquired specifically for its talent rather than its products or revenue, offers an alternative exit to an IPO or scaling.
Unlike the more traditional merger or acquisition, acquihires prioritize employees, sometimes bringing on entire teams. Discreetly done, these types of hires help corporations compete without the complexities of full integrations. Additionally, an acquihire, which can be less costly than a traditional acquisition, involves structuring the deal through stock or asset sales, with most value directed to employee retention packages. The cost hinges on the perceived value of the employees to the buyer, with monetary incentives like signing bonuses, stock option conversion, and new option packages, combined with restrictive covenant agreements, designed to ensure staff remain locked-in following the transaction with the buyer.
Market Data for Acquihires
The bar chart below illustrates the rise in acquihire deals from 2020 through July 2025, with Q1 and Q2 of 2025 showing increased activity compared to previous periods.
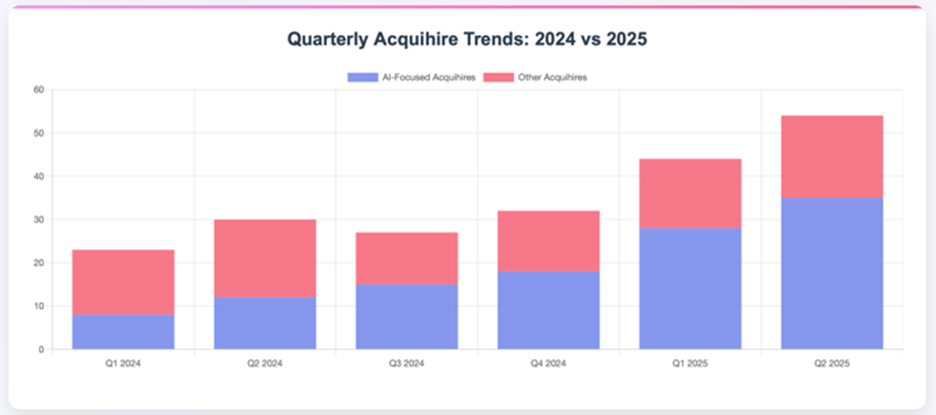
The data shows that after four years of being frozen out of the acquihire market by former FTC chair Lina Khan, big tech companies are back with a vengeance. The following chart compares acquihire activity of the six most prolific big tech buyers in 2024 compared to 2025, and we are barely halfway through the year:
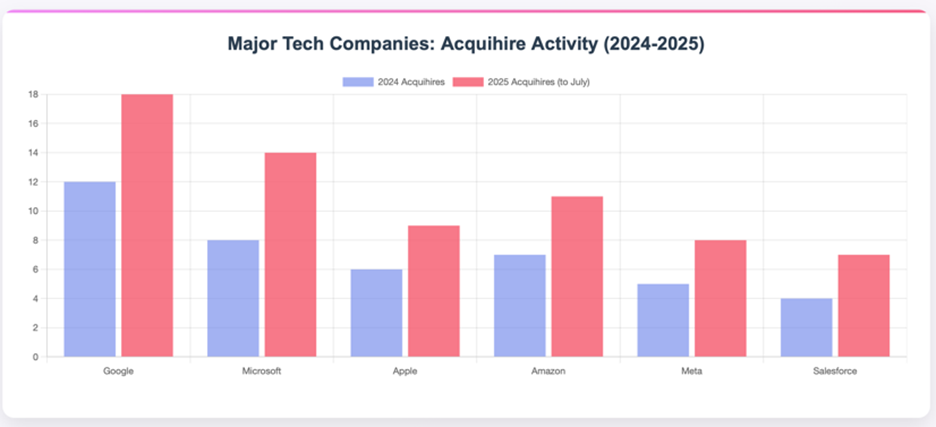
Several factors are driving this increased activity.
- Talent Availability: Layoffs have increased the pool of skilled tech workers, particularly those with niche expertise in AI, cybersecurity, and quantum computing. Upon layoff, these skilled tech workers often form or join new startups. Larger companies are targeting these startup talent pools through acquihires to secure specialized skills.
- AI-Driven Focus: The race to dominate AI is accelerating acquihire activity. Companies are acquiring startups or teams with advanced AI capabilities, including generative AI, machine learning, and natural language processing expertise, to stay competitive.
- Regulatory Clarity in Washington: While the new administration cannot be characterized as “tech friendly,” there seems to be a burgeoning understanding that mergers will be scrutinized for structural and vertical overlap but not shut down altogether as was the case under the prior administration.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Acquihires introduce legal challenges, requiring a team of attorneys who can advise on a wide variety of issues beyond the typical flurry of M&A contract issues, such as employment law, intellectual property (IP), compensation structures, and compliance.
Retention and Equity Challenges
Retention agreements are an important part of this process, with equity grants, signing bonuses, or extended vesting schedules to ensure talent retention. Legal counsel should review to be sure these incentives comply with prior obligations, such as stock option agreements, Simple Agreements for Future Equity (SAFEs), or investor rights from the startup’s cap table. Missteps can potentially land you in court and lead to disputes with former investors or employees.
The IP Minefield
IP rights are always a significant hurdle to a business transaction. In an acquihire situation, acquiring companies need to verify that incoming teams possess clean, transferable IP. Complications arise when code was developed pre-incorporation, uses improperly licensed open-source software, or involves co-ownership with universities, former employers, or contractors.
Compliance in a Regulated Landscape
Acquihires are becoming more and more visible to regulators. Cross-border deals require navigating local labor laws, tax structures, and other requirements, such as visa sponsorship requirements. Antitrust scrutiny may apply if the acquired startup posed a competitive threat. Compliance with GDPR and all other data privacy regulations must also be a consideration.
Strategic Implications
For corporate attorneys, legal advisors, and other deal professionals, proactive planning is essential to the successful execution of an acquihire. Acquihires are driven by talent retention as opposed to revenue or product synergies in traditional acquisitions. Advisors play a key role in structuring agreements that protect the acquiring company while ensuring key team members are incentivized to stay post-transaction. When done the right way, acquihiring provides a strategic edge. When mismanaged, it can lead to legal and financial liabilities.
As we progress into Fall 2025, and AI is continuing to shape the tech industry, acquihires remain a strategic lever for companies. Approached with diligence, they are a powerful way to grow and stay competitive. This model offers honorable (if not always lucrative) exits for founders and investors. Will it risk consolidating AI innovation within a few dominant players, sidelining employees, and narrowing the competitive landscape? This administration, like the last one, seems to be watching carefully to safeguard the competitive landscape while tampering down any new regulation.
Policymakers and regulators may be thinking about whether acquihiring fuels progress or stifles broader innovation, while in truth, Silicon Valley needs the surplus of AI companies to have soft landings (or big exits) to recycle capital deployed back into the startup ecosystem, which has been thirsty for exits since the end of ZIRP in 2022 (zero interest rate policy). The answer can redefine the very structure of the AI economy for decades.
Sources and data references
The author leveraged numerous publicly available data sources for the above-referenced statistics and charts:
- Layoffs.fyi – Tech layoffs tracker and database
- Crunchbase – Startup funding and acquisition data
- TechCrunch – Technology industry news and analysis
- McKinsey & Company – Technology trends outlook 2025
- Deloitte Insights – 2025 technology industry outlook
- Visual Capitalists – Big Tech hiring trends analysis
- Robert Half – Technology hiring trends report 2025
- CB Insights – Acquire market analysis and trends
- Tracxn – Corporate acquisition tracking (Google, Apple, Microsoft)
- CompTIA – State of the tech workforce 2024
- Korn Ferry – Talent acquisition trends 2025




 />i
/>i
